RainBO – Life Project for the assessment of climate change impact on urban areas
Brief
The project was developed in cooperation with Lepida Spa, Arpa ER, the Municipality of Bologna and the company MEEO.
Develop a monitoring infrastructure capable of combining hydrological and terrain models and rainfall data for more accurate prediction of extreme weather events in small basins and their potential impacts in urban areas (flash floods).
Project challenge
In particular, the project aimed to study the phenomenon of “rain bombs” (intense localised microbursts) in small basins through the implementation of innovative monitoring systems and a multi-channel software platform with on-line (early warning) and off-line (urban planning) operation, in order to increase the level of local resilience.
Solution
In collaboration with partners, NIER developed the RainBO platform which:
– supports territorial planning activities
– assists the handling of emergency responses
– provides a reliable system for early warning and monitoring in event scenarios.
Execution phases
C.1: Analysis of project requirements
C.2: Analysis, design and implementation of the monitoring infrastructure
C.3: Analysis, design and implementation of the RainBO platform prototype
C.4: Test and validation of the RainBO platform using Municipality of Bologna pilot case
C.5: Repeatability and transferability – Set up and management of the Advisory Board
D.1: Monitoring the impact of the project actions
E.1: Discosure and dissemination of results
Achieved results
Starting from the collection of georeferenced spatial data of the planned case studies and their normalisation, the platform interface was developed, within which the monitoring infrastructures, hydrological simulation models, historical data relating to significant hydraulic events and real-time data (measured, observed and simulated) were integrated.
On the basis of information useful for civil protection purposes, NIER developed an algorithm for calculating and simulating the vulnerability of the territory as a function of hydrogeological/hydraulic risk, so that when a forecast or adverse weather event is reported, the “early warning” module can effectively assess the most vulnerable structures to be alerted with priority.
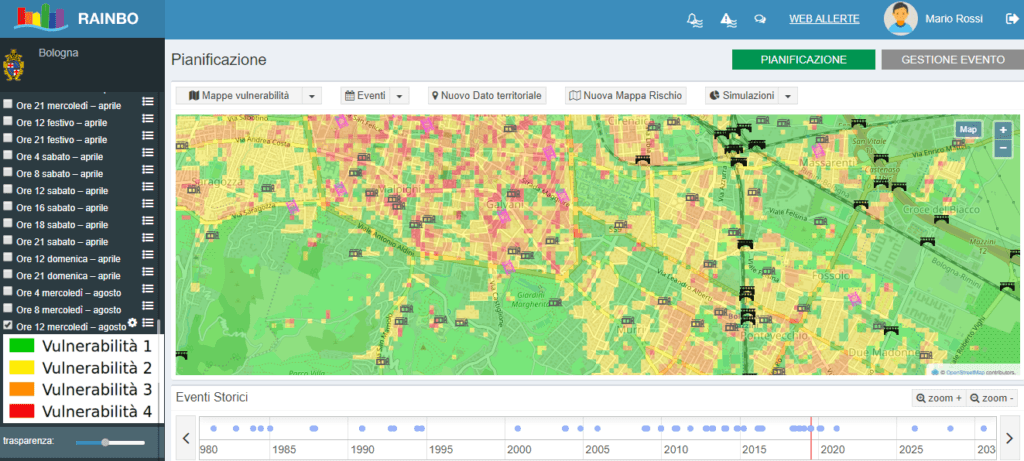
Hydraulic Risk Vulnerability Map

